Hearing loss is a prevalent and often misunderstood health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can occur at any age and can be caused by various factors. To better understand hearing loss and its implications, it is essential to familiarize ourselves with the different types of hearing loss, their unique characteristics, and available treatment options. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the three main types of hearing loss: conductive hearing loss, sensorineural hearing loss, and mixed hearing loss.
Conductive Hearing Loss:
Conductive hearing loss occurs when there is an obstruction or damage in the outer or middle ear, preventing sound waves from reaching the inner ear properly. Common causes of conductive hearing loss include ear infections, excessive earwax buildup, fluid in the middle ear, a perforated eardrum, or abnormalities in the ear’s bone structure.
Characteristics of Conductive Hearing Loss:
Sounds may appear muffled or faint.
Difficulty hearing low-pitched sounds.
Hearing loss is often unilateral (affecting one ear) but can be bilateral in some cases.
Temporary hearing loss can improve with medical treatment or removal of the blockage.
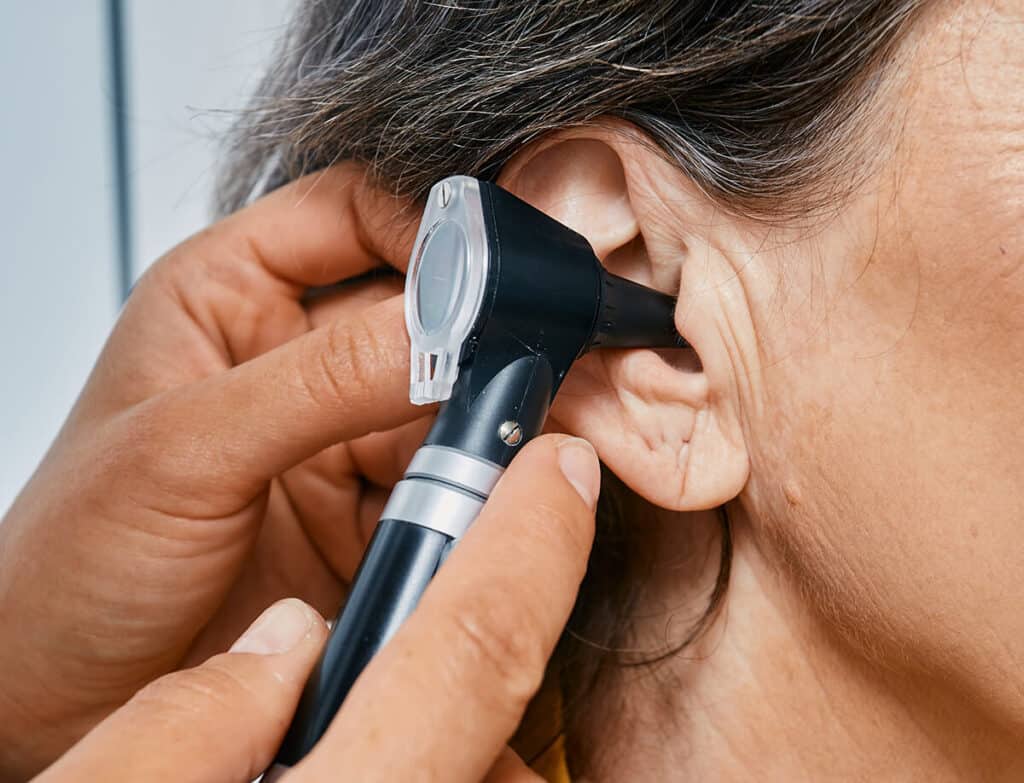
Treatment for Conductive Hearing Loss:
Fortunately, conductive hearing loss is often treatable and temporary. Medical interventions, such as antibiotics for infections or removal of earwax blockages, can restore hearing in many cases. If the conductive hearing loss is caused by structural abnormalities, surgical procedures may be necessary to correct the issue and restore proper hearing function.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss:
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common type of hearing impairment. It occurs when there is damage to the hair cells in the inner ear (cochlea) or problems with the auditory nerve, which transmits sound signals from the inner ear to the brain.
Sensorineural hearing loss can be caused by a variety of factors, including aging, exposure to loud noises, genetics, certain medications, infections, and head injuries.
Characteristics of Sensorineural Hearing Loss:
Difficulty understanding speech, especially in noisy environments.
Inability to hear soft or faint sounds.
Tinnitus, the perception of ringing, buzzing, or humming in the ears, is a common symptom of sensorineural hearing loss.
Treatment for Sensorineural Hearing Loss:
Sensorineural hearing loss is typically permanent and irreversible. In most cases, the damaged hair cells cannot be repaired or regenerated. However, hearing aids and cochlear implants are highly effective in managing sensorineural hearing loss. Hearing aid amplify sounds, making them audible to the individual, while cochlear implants bypass the damaged hair cells and directly stimulate the auditory nerve, allowing for improved hearing.
Mixed Hearing Loss:
Mixed hearing loss is a combination of both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. It occurs when there are issues in both the outer/middle ear and the inner ear or auditory nerve. Mixed hearing loss can result from chronic ear infections, trauma, or age-related hearing loss compounded by other conditions.

Characteristics of Mixed Hearing Loss:
Individuals with mixed hearing loss may exhibit symptoms of both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, depending on the degree of impairment in each part of the ear.
The presence of conductive and sensorineural components can complicate the diagnosis and treatment of mixed hearing loss.
Treatment for Mixed Hearing Loss:
Treatment for mixed hearing loss may involve a combination of medical intervention, such as surgery or medication, and the use of hearing aids or cochlear implants to address both the conductive and sensorineural components of the impairment. Treatment plans are typically tailored to the specific underlying causes and the severity of the hearing loss in each part of the ear.
In Conclusion: Hearing loss is a complex and multifaceted condition that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Understanding the different types of hearing loss is essential in seeking timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. If you suspect hearing loss in yourself or a loved one, it is crucial to consult with a qualified audiologist or hearing care professional. Early intervention and the use of hearing aids or other hearing devices can significantly improve communication and overall well-being, allowing individuals to reconnect with the world of sound and lead fulfilling lives. By encouraging greater awareness of hearing loss and its types, we can promote better hearing health for all.





